Green Fuels

Concept Of Green Fuels
Green energy, or green power, represents the energy sources that have the least amount of environmental impact.
These types of energy sources don’t release harmful carbon emissions, meaning they’re effective at helping you reduce your carbon footprint. some examples of green energy include electricity produced from solar, wind, geothermal, and other low-impact sources.
All green energy resources are renewable, not all renewable resources are considered green. For example, wind power is green and renewable; burning wood is renewable (because you can grow more trees) but not green (because it releases pollution into the atmosphere).
Alternative fuels or Sustainable fuels
Green fuels, also known as alternative fuels or sustainable fuels, refer to a diverse group of energy sources that are produced using environmentally friendly and renewable methods. These fuels are considered “green” because they have a significantly lower environmental impact compared to traditional fossil fuels like coal, oil, and natural gas.
These fuels are designed to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, air pollution, and dependence on fossil fuels.
Importance Of Green Fuels
Mitigation Of Climate Change:
Green fuels play a pivotal role in mitigating climate change. by reducing greenhouse gas emissions,
particularly carbon dioxide (CO2), which helps slow down global warming and its adverse effects. this is vital for preserving the planet’s ecosystems and avoiding catastrophic climate-related events.
Air quality improvement
Traditional fossil fuels release a host of pollutants, such as sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate
matter, which contribute to poor air quality and related health issues. Green fuels produce fewer or no harmful emissions, leading to cleaner air and improved public health. Green fuels produce fewer pollutants and particulate matter when burned, leading to improved air quality and better respiratory health for communities.

Energy security
Green fuels decrease reliance on fossil fuels, many of which are imported, and reduce a nation’s vulnerability to energy supply disruptions and price fluctuations. this enhances energy security and economic stability. Green fuels can be produced locally, reducing the dependency on imported fossil fuels. This enhances energy security and promotes sustainable development.
Renewable resource availability
Unlike fossil fuels, which are finite and depleting resources, green fuels are sourced from renewable materials or energy sources. This ensures a more sustainable and long-term energy supply.

It is time for a sustainable energy policy that puts consumers, the environment, human health, and peace first.
Reduction Of Energy-Related Conflicts
Fossil fuels have often been a source of conflict and geopolitical tensions. shifting to green fuels can help reduce these conflicts by decreasing the competition for limited fossil fuel resources.
Economic benefits
The production and use of green fuels can create job opportunities and stimulate economic growth in the renewable energy sector. It can also significantly reduce healthcare costs associated with air pollution and environmental damage.
Types Of Green Fuels
Various types of green fuels are available like
- Biofuels
- Hydrogen fuels
BioFuels
The most common and widely discussed and researched among them is biofuels. The term biofuels applies to liquid fuels and blending components produced from biomass material called feedstock. Most biofuels are used as transportation fuels, but they may also be used for heating and electricity generation.
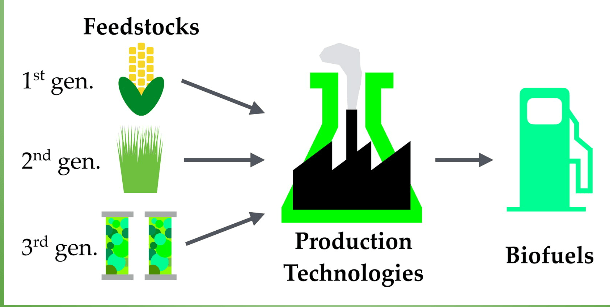
Hydrogen fuel
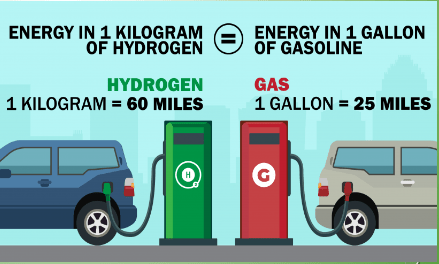
Hydrogen is the lightest element in the universe and the most abundant, so on paper, hydrogen fuel has a lot going for it. Although it rarely exists on its own on Earth, it can be produced using clean energy to split essentially inexhaustible water molecules, producing only oxygen as a by-product. Hydrogen acts as a chemical energy carrier, rather like oil or gas, that can be piped or transported to where it is needed. It stores three times as much energy per unit of mass as conventional petrol, and when it “burns” in air –
releasing that stored energy – it simply combines with oxygen to produce water again.
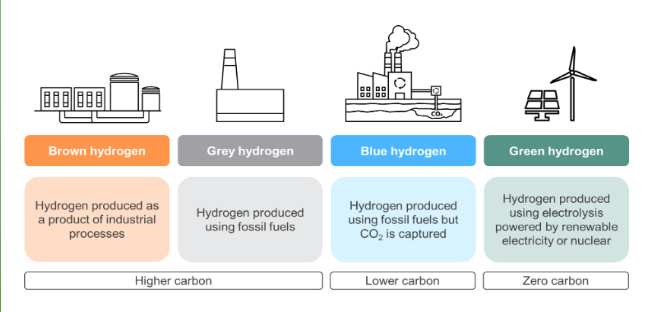
Several countries and blocs have recently launched hydrogen strategies, with the European Union’s pro-green hydrogen plan being the most notable one in July 2020. However, bringing down the cost of blue and green hydrogen to compete with the polluting grey hydrogen will require many years of government support and huge investments. According to Bloomberg New Energy Finance, this will cost $150 billion over a decade.




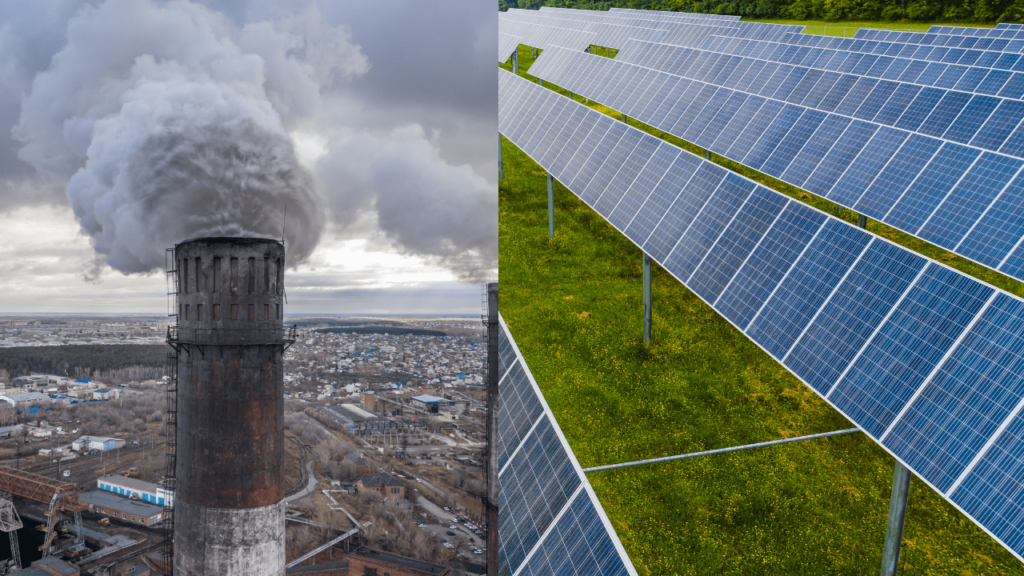
Green Fuel VS Fossil Fuels
| Green Fuels | fossil fuels |
| It is a renewable energy source. | It is a non-renewable energy source. |
| It is made from plants and organic waste | It is made from organisms that died millions of years ago |
| They have toxic effects on human health | They have toxic effects on human health |
| No or minimal emission of GHG. | High emission of GHG. |

Challenges For Green Fuels
Production costs
Many green fuels, especially advanced biofuels like cellulosic ethanol and algal biofuels, can be expensive to produce compared to conventional fossil fuels.
Technology Development
Developing and optimizing production technologies for green fuels is an ongoing process. Advancements are needed to make these fuels more efficient, cost-effective, and sustainable.
Market Competition:
Green Fuels face competition from established fossil fuels industries that have substantial resources and
influence. market dynamics can make it challenging for green fuels to gain a significant market share.
